Describe the Structure of an Osteon
Blood vessels run throughout central canals in compact bone. Osteon basic unit of mature compact bone osteoblasts immature bone cells stem cells osteoid matrix produced by osteoblasts osteoprogenitor cells stem cells that divide to produce osteoblasts.

Structure Of Bones Biology For Majors Ii
In trabecular bone the building block is.

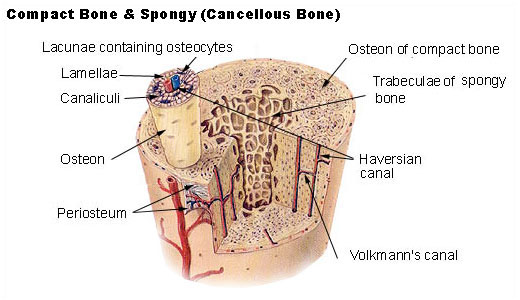
. Name three types of lamellae found in compact. A structural unit of compact bone. An osteon refers to a unit of compact bone that includes a central canal and the concentric layers of lamellae and osteocytes surrounding the canal.
An osteon comprises a long hollow central canal that is surrounded by concentric layers called lamallae. They are aligned parallel to the long axis of the bone. Each group of concentric circles each tree makes up the microscopic structural unit of compact bone called an osteon this is also called a Haversian system.
Describe the research on bone density related to aging and exercise. It consists of concentric rings or lamellae surrounding the central canal or the Haversian canal. The Structure of Compact Bone Osteon is the basic unit Osteocytes are arranged in concentric lamellae Around a central canal containing blood vessels.
Each osteon is composed of concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae singular lamella. The hollow center of an osteon also known as a Haversian canal. Their length is often hard to define but estimates vary from several millimeters to around 1 centimeter.
Although cortical bone provides the majority of mechanical strength for a bone there are few studies focusing on. Between the rings of matrix the bone cells osteocytes are located in spaces called lacunae. The osteon or haversian system həˈvɜːrʒən named for Clopton Havers is the fundamental functional unit of much compact bone.
The blood vessels and nerves that are housed within these canals can be viewed in the. Each osteon has a cylindrical structure that consists of the following components. This central canal is referred to as the Haversian canal.
6-1 Describe the primary functions of the skeletal system. Each osteon consists of lamellae which are layers of compact matrix that surround a central canal called the Haversian canal. Assist in fracture repair osteoclasts secrete acids.
Thousands of stacked osteons make up cortical bone. Only because of the joint action of the skeleton and musclesour body we are able to move and. Bone is laid down around the central canal in concentric rings called lamellae.
With the osteon at the center of the field of view increase the magnification. Osteons are cylindrical structures that contain a mineral matrix and living osteocytes connected by canaliculi which transport blood. Osteons are roughly cylindrical structures that are typically between 025 mm and 035 mm in diameter.
Its shape approximates a hollow cylinder too but is a hundred times smaller than its long bone host. Running down the center of each osteon is the central canal or Haversian canal which contains blood vessels nerves and lymphatic vessels. The central Haversian canals will be the largest holes visible in the sample.
The collagen fibers of adjacent lamallae run at perpendicular angles to each other allowing osteons to resist. Vessels are surrounded by 4-20 rings of lamellae. Osteon is a part of rigid skeletal tissue the bone.
2Perforating canalsVolkmanns canals- lie at right angles to the long. The long axis of the osteon is parallel to the long axis of the bone. 1central canalHaversian canal- contains the artery vein and nerve fibers.
Structure and function Structure of the bone. Structure Turnover and Regeneration Abstract Bone is composed of dense and solid cortical bone and honeycomb-like trabecular bone. The central canal contains blood vessels lymphatic vessels lymphatic vessels and nerves.
Osteon is the structural unit of bone. The osteon consists of a central canal called the osteonic haversian canal which is surrounded by concentric rings lamellae of matrix. Osteocytes live in lacunae that are between each ring of lamella.
Identify and explain the roles of the cells and blood vessels found within an osteon. Forensic Fractography of Bone A New Approach to Skeletal Trauma Analysis. In this section we are starting with a closer look at the bone tissues and cells.
Describe the structure of compact bone. Due to this structure bone tends to behave mechanically like a fiber-reinforced composite where lamellar bone is the matrix and the osteons are the reinforcing fibers Burr et al. In this video we discuss the structure of bone tissue and the components of bones.
In the previous section you were introduced to basic bone structure and functions. Each ring of the osteon is made of collagen and calcified matrix and is called a lamella plural lamellae. Osteons are formations characteristic of mature bone and take shape during the process of bone remodeling or renewal.
An osteon is composed of many concentric. The basic bone building block is the osteon or Haversian system. Click again to see term.
View the full answer Previous question Next question. New bone may also take this structure osteon the chief structural unit of compact cortical bone consisting of concentric bone layers called lamellae which surround a long hollow passageway the Haversian canal named for Clopton Havers a 17th-century. We also discuss what are osteons what are canaliculi what are trabecula.
The combination of organic 30-40 and inorganic 60-70 of substances is a feature of the. The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon or Haversian system.
Seer Training Structure Of Bone Tissue

Osteon Development And Structure Stock Illustration 12234766 Pixta
5 Structure Of The Osteons Of Cortical Bone Junqueira And Carneiro 1992 Download Scientific Diagram
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Describe the Structure of an Osteon"
Posting Komentar